11 min read
Media Analysis: What is it, how does it work and why is it important?
Key Takeways
- What is Media analysis
- What are the approaches to media analysis?
- How to do media analysis step by step?
- Where and why is media analysis used?
- Practical tips and the best tools for media analysis
- Recommended tools
In today’s information-saturated landscape, businesses, organizations, and decision-makers rely on media analytics to extract meaningful insights from the vast flow of digital content. From monitoring real-time global events to understanding shifts in public opinion, media analytics enables companies to navigate an increasingly complex environment.
However, with the rapid proliferation of online media, social platforms, and fragmented news sources, traditional media tracking is no longer enough. Advanced AI-driven solutions—like those provided by Semantic Visions—are revolutionizing media intelligence by offering deep, real-time analysis of global narratives across multiple languages and regions.
This article explores the methodologies, applications, and tools behind media analytics, with a special focus on how leading-edge solutions like Semantic Visions help businesses and institutions stay ahead of risks, market trends, and reputational threats.
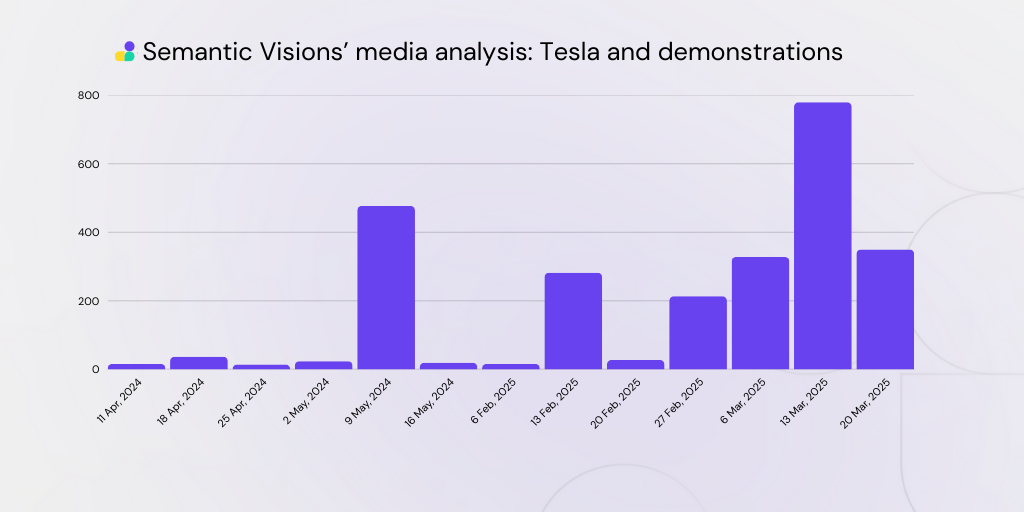
| The peaks explained, with representative article headlines in English: MAY 2024 Arson Attacks: Left Extremists Promise ‘Week of Action’ Against Teslas MAY 2024 Climate protestors clash with police outside Tesla’s German gigafactory FEB 2025 The anti-Musk protest movement is expected to ramp up with Congress on recess MAR 2025 9 arrested at New York Tesla dealership amid anti-Musk protests MAR 2025 Canadians in several cities join ‘Tesla Takedown’ protests against Musk, Trump MAR 2025 3 people face federal charges for Tesla attacks. Are such acts domestic terrorism? MAR 2025 ‘Tesla Takedown’ protesters planning ‘biggest day of action’ |
What is the definition of media analysis?
Media analysis, also known as media analytics, is the systematic process of collecting, processing, and analyzing data from various media sources to gain insights into public opinion, trends, competitor activities, and other relevant information. This is a form of media analysis research. These sources can include traditional media (newspapers, magazines, television, radio), online news websites, social media platforms (Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, LinkedIn, etc.), blogs, forums, review sites, and other online content. The core goal is to analyse media text and extract meaningful data.
Sources:
| Traditional media – Newspapers, television, radio Digital news – Online publications, blogs, press releases Social media – Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, TikTok, Reddit Specialized forums & alternative sources |
The core purpose of media analysis is to transform raw, unstructured data into structured, actionable intelligence. This involves identifying patterns, trends, sentiments, key themes, and relationships within the data. Media analysis, and specifically media content analysis, goes beyond simply tracking mentions or counting keywords; it delves into the context and meaning of the content to provide a deeper understanding of the underlying narratives and dynamics.
This understanding is crucial for:
- Reputation Management
- Crisis Communication
- Competitive Intelligence
- Market Research
- Campaign Measurement
- Political Analysis
- Journalism and Research
Key differences between Media analysis and Media monitoring
While the terms “media monitoring” and “media analysis” are sometimes used interchangeably, they represent distinct processes with different objectives. Media monitoring is primarily concerned with tracking mentions of specific keywords, brands, or topics across various media channels. It’s a largely quantitative process focused on collecting data – identifying where and how often something is being said. Media analysis, on the other hand, goes beyond simple tracking. It involves a deeper, more interpretive process of analyzing the collected data to understand its meaning, context, and implications. Media analysis uses both quantitative and qualitative methods to uncover patterns, trends, sentiments, and narratives, ultimately transforming raw data into actionable intelligence. In short, media monitoring tells you what is being said, while media analysis tells you why it’s being said and what it means.
How to analyze media? Different approaches to media analysis
There are three primary approaches to media analysis: quantitative, qualitative, and a combination of both. These are considered standard media analysis methods.
Quantitative Media Analysis
This approach focuses on measurable data and statistical analysis. It involves counting the frequency of keywords, mentions, hashtags, and other quantifiable elements within a dataset. This data often forms the basis of a media analysis report.
Quantitative analysis can reveal:
- Volume of Mentions
- Reach
- Share of Voice
- Sentiment Analysis
- Trend Analysis
Quantitative analysis is particularly useful for identifying large-scale patterns and trends. However, it may lack the depth and nuance to fully understand the underlying reasons.
Qualitative Media Analysis
This approach focuses on the content and context of the media coverage. It involves a close reading and interpretation of text, images, and videos to understand the underlying messages, themes, and narratives. This is often called textual media analysis.
Qualitative analysis can reveal:
- Key Themes and Topics
- Framing
- Narrative Analysis
- Discourse Analysis
- Contextual Understanding
Qualitative analysis provides rich, in-depth insights. However, it can be time-consuming and subjective.
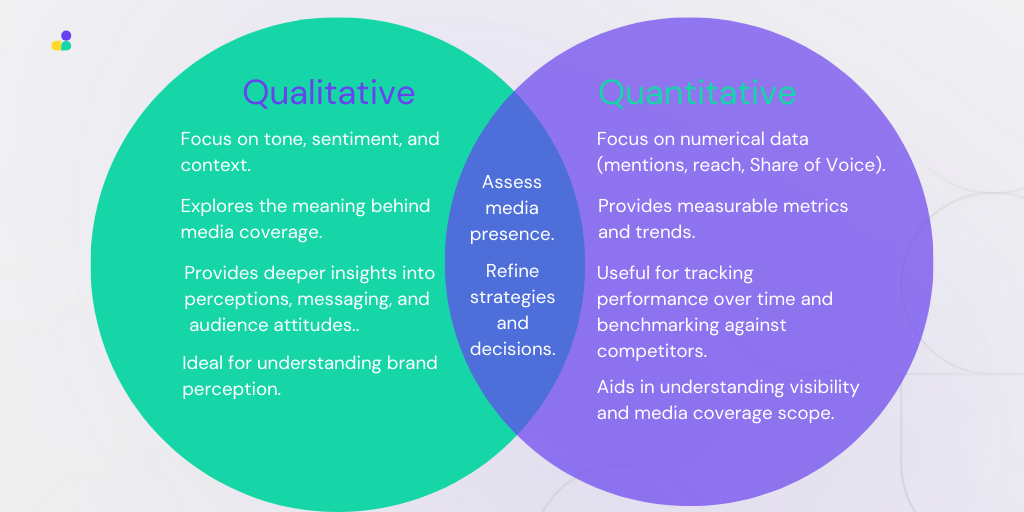
Combined Media Analysis Method (Mixed approach)
The most effective media analysis often combines both quantitative and qualitative methods. This allows researchers to leverage the strengths of both approaches, providing a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding. Quantitative analysis can identify trends, and qualitative analysis can then explore those trends in more detail. This integrated approach is often facilitated by advanced media intelligence platforms, like those offered by Semantic Visions.
The Scope of Semantic Visions in Media Analytics: A Data-Driven Approach
In today’s rapidly evolving media landscape, businesses, financial institutions, and governments face an overwhelming flow of information. The challenge is not just tracking mentions but understanding the deeper narratives, detecting risks early, and identifying opportunities.
This is where Semantic Visions comes into play. By combining quantitative data analysis with qualitative contextual insights, our AI-powered media analysis platform provides a holistic, real-time view of global media narratives.
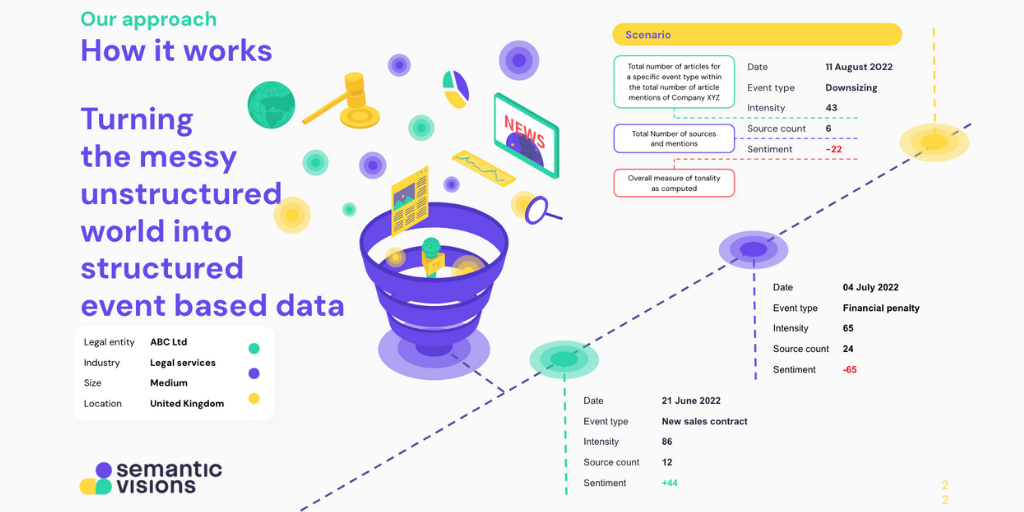
Why Traditional Media Monitoring is No Longer Enough
Most conventional media monitoring tools rely on basic keyword tracking, sentiment classification, and volume analysis. While these methods provide surface-level insights, they often fail to:
- Capture the full scope of global media narratives.
- Detect emerging risks before they escalate.
- Connect real-world events to business implications.
At Semantic Visions, we take media analysis beyond traditional monitoring, leveraging cutting-edge AI, Natural Language Processing (NLP), and machine learning to analyze 100,000+ digital news sources in 12 languages.
Applications of Semantic Visions’ Media Analytics
- Financial & Investment Risk Monitoring:
- Detecting market-moving events.
- Understanding investor sentiment shifts.
- Supply Chain & ESG Risk Management:
- Mapping supply chain vulnerabilities.
- Monitoring sustainability and compliance risks.

| Understanding Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance is essential for businesses committed to responsible growth. Semantic Visions’ Free Responsible Business Index dataset provides valuable insights into how companies are perceived in global media, helping investors, policymakers, and businesses make informed decisions. Access the free dataset and explore the evolving ESG landscape with data-driven clarity. |
- Corporate Reputation & Crisis Management:
- Early identification of reputational risks.
- Preventing misinformation escalations.
- Geopolitical & Policy Monitoring:
- Analyzing government decisions and policy shifts.
- Tracking emerging political risks.
How to Do Media Analysis Step by Step?
A robust media analysis, and the creation of a thorough media analysis report, typically involves the following steps:
- Define Objectives and Scope
Clearly define the research question(s) and the scope of the analysis. - Data Collection
Gather relevant data. Semantic Visions’ platform automates much of this. - Data Cleaning and Preparation
Clean and prepare the data. - Quantitative Analysis (if applicable)
Apply appropriate statistical methods. - Qualitative Analysis (if applicable)
Conduct a close reading and interpretation. This is where you would analyse media text in detail. - Integration and Interpretation
Integrate the findings and interpret the results. - Reporting and Visualization
Present the findings clearly. Semantic Visions’ reporting capabilities are valuable here. - From Insight to Action
Translate findings into concrete recommendations.
Where and Why is Media Analysis Used?
Media analysis has a wide range of applications across various sectors:
- Business and Marketing
Brand monitoring, reputation management, competitive intelligence, market research, and campaign measurement. - Public Relations (PR)
Tracking media coverage, managing crises, and measuring campaign effectiveness. - Politics and Government
Tracking public opinion and analyzing political discourse. - Journalism
Supporting evidence-based reporting. - Academia and Research
Studying social, political, and cultural phenomena. - Crisis communication
Practical Tips and the Best Tools for Media Analysis
- Define clear objectives
Start with a clear understanding of your goals for the media analysis. - Choose the right tools
Select tools appropriate for your needs. - Use a combination of methods
Combine quantitative and qualitative methods. - Be aware of bias
Be mindful of potential biases. - Stay up-to-date
The media landscape is constantly evolving. - Consider professional expertise
For complex projects, consider working with a media analysis expert, like Semantic Visions.
Recommended Tools
- Semantic Visions Platform
A comprehensive media intelligence platform. - Cision
A provider of PR and marketing communication software. - Talkwalker
A social listening and analytics platform. - Brandwatch
A social media intelligence platform. - Google Alerts
A free tool for tracking keyword mentions.
Comparison of Leading Media Intelligence Tools
Comparison of Leading Media Intelligence Tools
| Feature | Semantic Visions | Cision | Talkwalker | Brandwatch | Google Alerts |
| Global Media Coverage | 100,000+ sources (news, blogs, regulatory) | News & PR-focused sources | News, social media, broadcast | Social media-heavy + some news | Basic web & news monitoring |
| Languages Supported | 12+ languages | 10+ languages | 25+ languages | 20+ languages | Limited |
| AI & NLP-Based Analysis | ✅ Advanced AI & NLP | ❌ Limited AI capabilities | ✅ AI-powered insights | ✅ AI-assisted insights | ❌ No AI |
| Real-Time Monitoring | ✅ Real-time alerts | ✅ PR-focused monitoring | ✅ Real-time analysis | ✅ Real-time updates | ✅ Simple alerts |
| Sentiment Analysis | ✅ In-depth sentiment shifts | ✅ Sentiment scoring | ✅ Sentiment & emotion detection | ✅ Sentiment analysis | ❌ No sentiment analysis |
| Social Media Listening | ❌ Limited focus on social media | ✅ Integrated social media | ✅ Strong in social analytics | ✅ Best for social media monitoring | ❌ No social media tracking |
| Crisis Detection | ✅ Early warning crisis detection | ❌ Weak crisis detection | ✅ Crisis alerts | ❌ No crisis detection | ❌ No crisis detection |
| Competitive Intelligence | ✅ Deep competitor tracking | ✅ Media-focused competitor tracking | ✅ Brand & campaign tracking | ✅ Brand perception tracking | ❌ No competitor insights |
| Geopolitical & Policy Tracking | ✅ Global policy & economic risk monitoring | ❌ No geopolitical insights | ❌ Limited policy risk monitoring | ❌ No geopolitical insights | ❌ No policy risk analysis |
| Supply Chain Risk Mapping | ✅ Multi-tier supply chain mapping | ❌ No supply chain intelligence | ❌ No supply chain tracking | ❌ No supply chain monitoring | ❌ No supply chain monitoring |
Semantic Visions
is the most comprehensive media intelligence tool, excelling in predictive analytics, crisis detection, geopolitical monitoring, and supply chain risk tracking.Talkwalker, and Brandwatch
are strong in social media listening, whereas Semantic Visions specializes in deep media intelligence and risk assessment.Google Alerts
is free, but extremely limited in capabilities.Cision
is strong in PR and communication monitoring, but lack predictive analytics or strategic intelligence features.
| To stay ahead in an increasingly complex media landscape, businesses need more than just monitoring—they need actionable intelligence. Semantic Visions goes beyond traditional tracking, delivering predictive insights, crisis detection, and global risk analysis to help organizations make smarter, data-driven decisions. Request a demo to see how our AI-driven platform transforms media data into a strategic advantage. |
Conclusion
Media analysis is a powerful tool for understanding the complex and ever-evolving media landscape. By systematically collecting, processing, and analyzing media data, valuable insights can be gained. The key is to choose the right approach, utilize appropriate tools, and, when necessary, leverage the expertise of specialized providers like Semantic Visions. This guide provides insights into how to do a media analysis.
Ready to unlock the power of media analysis and generate your own media analysis report? Contact us today.
FAQs:
- What’s the difference between media analysis and social media listening?
Social media listening is a subset of media analysis. Social media listening focuses specifically on gathering and analyzing data from social media platforms. Media analysis, in contrast, is broader. It encompasses all types of media, including traditional and online sources, in addition to social media.
- How can media analysis help with crisis communication?
Media analysis is crucial for effective crisis communication because it allows organizations to detect crises early through real-time monitoring. It helps understand public perception via sentiment and qualitative analysis. It also allows to track the spread of misinformation. Finally, it helps to measure the effectiveness of response efforts.
- What kind of data does Semantic Visions’ platform analyze?
Semantic Visions’ platform specializes in analyzing a wide range of structured and unstructured data from digital sources, globally and in multiple languages. Their core expertise lies in handling vast amounts of unstructured text data from online news and the open web. They also integrate structured data for a comprehensive view. Semantic Visions leverages advanced AI and NLP to extract meaning.
- What level of technical expertise is required to use media analysis tools?
The level of technical expertise varies depending on the tool. Some tools, like Google Alerts, are very user-friendly. More sophisticated platforms, like Semantic Visions’, offer advanced features that may require some data analysis knowledge, but also offer user-friendly interfaces.
- Is media analysis ethical?
Yes, if it is conducted with respect to the privacy of individuals and to laws. Media analysis relies on collecting publicly available data. Ethical media analysis is about using this data responsibly and transparently. It also involves respecting individual privacy and complying with all applicable laws.